The research team from Huazhong Agricultural University (HZAU), led by Mei Zhinan and Yang Qingyong, professors from the National Key Laboratory for Germplasm Innovation & Utilization of Horticultural Crops and the Sustainable Use of Medicinal Plant Resources team of HZAU, has recently published their groundbreaking research in Nucleic Acids Research.
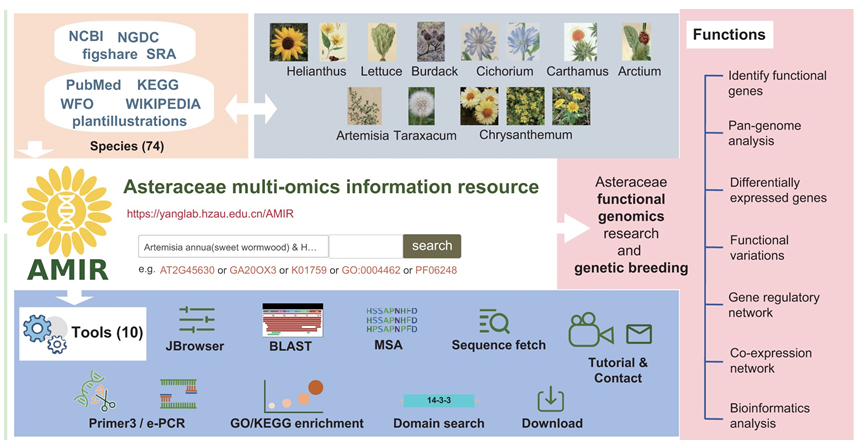
The paper, titled "AMIR: a multi-omics data platform for Asteraceae plants genetics and breeding research", introduces the Asteraceae Multi-omics Information Resource (AMIR), a comprehensive platform for data integration, analysis and visualization. This database yanglab.hzau.edu.cn/AMIR aims to support functional gene research and optimize breeding strategies for Asteraceae plants.
The Asteraceae family, one of the most important groups of angiosperms, includes numerous economically vital crops that can be categorized in four groups: oil crops like sunflower; leafy vegetables, like lettuce; ornamental flowers, like marigolds; and medicinal plants such as mugwort, artemisia, and chrysanthemum.
However, the complexity of Asteraceae genomes, combined with the lack of integrated data and user-friendly analysis tools, has made post-genomic research in this family particularly challenging and labor-intensive.
The AMIR database integrates multi-omics data from 74 Asteraceae species, including 132 genomes, 3,897 transcriptome samples, over 42.76 million variant data points, and more than 15,000 metabolic gene annotations. All data are standardized and unified for easier analysis.
The database features six major sections: genome and gene annotations, pan-genomes and cross-species comparisons, transcriptomic analysis, genetic variation and association analysis, metabolic pathways, and gene regulatory networks.
A researcher team from Huazhong Agricultural University publishes their research in Nucleic Acids Research.[Photo/news.hzau.edu.cn]
Additionally, integrated tools and data download options are provided to assist researchers in quickly analyzing gene associations, identifying candidate genes linked to key traits, and interpreting important metabolic pathways in Asteraceae plants.
Using the AMIR platform, researchers discovered that the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGR) gene is conserved across 43 Asteraceae species. They also mapped the conserved regions and evolutionary relationships of the HMGR gene across various Asteraceae species, offering valuable data for further research into its role in Asteraceae plant metabolism.
In the differential expression analysis module of the AMIR platform, the team analyzed gene expression differences under various experimental conditions and used GO/KEGG enrichment analysis tools to identify metabolic pathways associated with plant defense mechanisms. This functionality demonstrates AMIR’s potential in plant disease research and breeding for disease resistance.
Furthermore, through the SNP and InDel variation module, researchers can explore genetic variations in specific genes and analyze the relationship between these variations and gene expression. This module supports genome-wide association studies, helping to identify candidate genes linked to specific stress tolerance traits or the synthesis of medicinal components, making it an essential tool for molecular marker-assisted breeding in Asteraceae plants.
The AMIR database was developed by PhD students from the College of Informatics, including postdoctoral researcher Liu Dongxu, Luo Chengfang, Chen Xiang, Mao Hongxia, Li Jiawei, Zhang Linna and master's students Dai Rui and Huang Xiaoyan, along with PhD student He Lin from the College of Plant Sciences & Technology.
Mei Zhinan and Yang Qingyong served as the corresponding authors of the study.
The research was supported by various funding sources, including the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the High-Quality Seed Industry Development Project of Hubei Province, and the Basic Research Fund of HZAU, with computing platform support from HZAU's National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement.